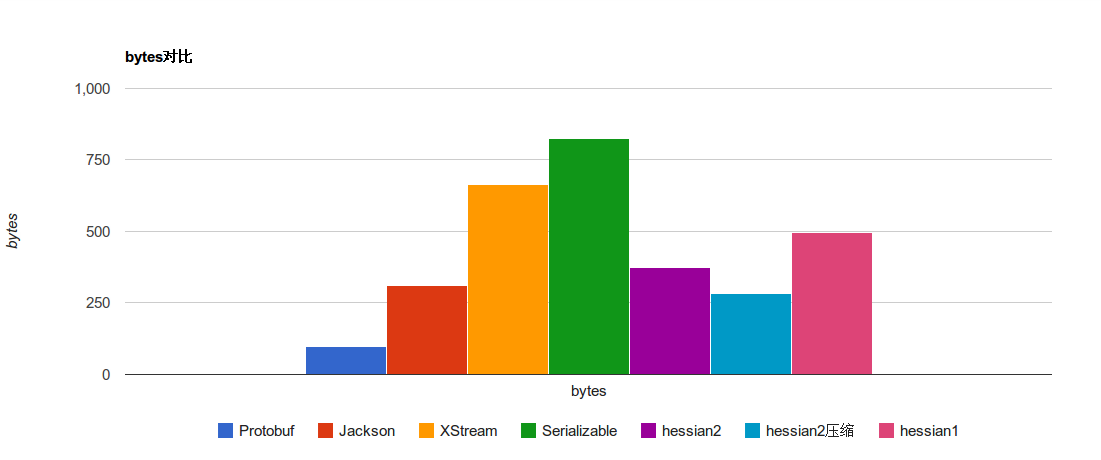
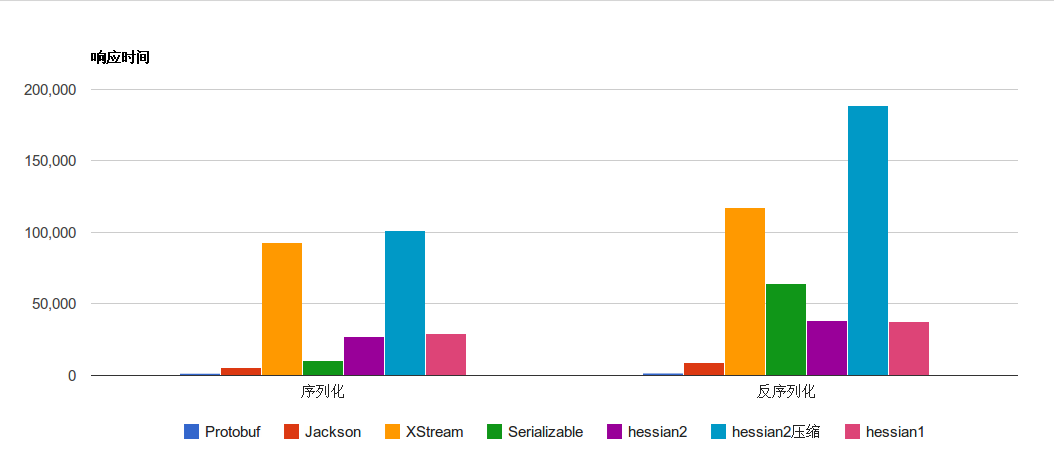
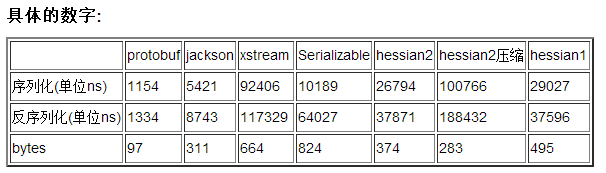
protocol buffer与其他几项序列化方案对比
windows安装protocol buffer编译器protoc
编译器下载地址: https://github.com/google/protobuf/releases
1. 下载protoc-x.x.x-win32.zip
2. 解压得到protoc.exe,这个是protobuf的编译器
3. 如果你需要在任意目录下都可以调用protobuf的编译器,可以在环境变量中配置path变量,在其中加入protoc.exe的目录。
创建maven项目,编写编译proto文件
- 在pom.xml中加入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.protobuf</groupId>
<artifactId>protobuf-java</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 编写XXX.proto文件
新建addressbook.proto文件,编辑内容
语法可参考: protocol-buffer介绍
syntax = "proto2";
package tutorial;
option java_package = "com.sylar.protocol";
option java_outer_classname = "AddressBookProtos";
message Person {
required string name = 1;
required int32 id = 2;
optional string email = 3;
enum PhoneType {
MOBILE = 0;
HOME = 1;
WORK = 2;
}
message PhoneNumber {
required string number = 1;
optional PhoneType type = 2 [default = HOME];
}
repeated PhoneNumber phones = 4;
}
message AddressBook {
repeated Person people = 1;
}
- 编译addressbook.proto
protoc -I=[proto文件所在目录] --java_out=[编译结果输出目录] xxxx.proto
我的项目结构
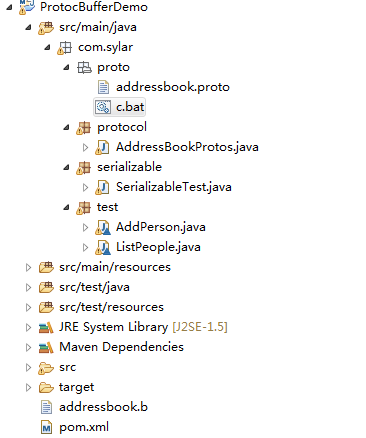
命令: protoc -I=./ --java_out=../../../ ./addressbook.proto
java api调用
- 创建对象
public static AddressBookProtos.Person build() { AddressBookProtos.Person.Builder personBuilder = AddressBookProtos.Person.newBuilder(); personBuilder.setId(1000); personBuilder.setName("张三"); personBuilder.setEmail("test@gmail.com"); AddressBookProtos.Person.PhoneNumber.Builder phone = AddressBookProtos.Person.PhoneNumber.newBuilder(); phone.setNumber("18610000000"); personBuilder.addPhones(phone); AddressBookProtos.Person person = personBuilder.build(); return person; } - 序列化方式1
public static void serializable1(AddressBookProtos.Person person) throws InvalidProtocolBufferException{
//第一种方式
//序列化
byte[] data = person.toByteArray();//获取字节数组,适用于SOCKET或者保存在磁盘。
//反序列化
AddressBookProtos.Person result = AddressBookProtos.Person.parseFrom(data);
System.out.println(result.getName());
}
- 序列化方式2
public static void serializable2(AddressBookProtos.Person person) throws Exception {
//第二种序列化:粘包,将一个或者多个protobuf对象字节写入stream。
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//生成一个由:[字节长度][字节数据]组成的package。特别适合RPC场景
person.writeDelimitedTo(byteArrayOutputStream);
//反序列化,从steam中读取一个或者多个protobuf字节对象
ByteArrayInputStream byteArrayInputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(byteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray());
AddressBookProtos.Person result = AddressBookProtos.Person.parseDelimitedFrom(byteArrayInputStream);
System.out.println(result.getEmail());
}
- 序列化方式3
public static void serializable3(AddressBookProtos.Person person) throws Exception {
//第三种序列化,写入文件或者Socket
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("addressbook.b"));
person.writeTo(fileOutputStream);
fileOutputStream.close();
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("addressbook.b"));
AddressBookProtos.Person result = AddressBookProtos.Person.parseFrom(fileInputStream);
System.out.println(result.getId());
}
- 测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
AddressBookProtos.Person person = SerializableTest.build();
serializable1(person);
serializable2(person);
serializable3(person);
}
6. 结果
张三
test@gmail.com
1000
官例
由于上面的addressbook.proto也由官方例子而来,所以可以直接测试官方贴出的代码
AddPerson.java
class AddPerson {
// This function fills in a Person message based on user input.
static Person PromptForAddress(BufferedReader stdin, PrintStream stdout) throws IOException {
Person.Builder person = Person.newBuilder();
stdout.print("Enter person ID: ");
person.setId(Integer.valueOf(stdin.readLine()));
stdout.print("Enter name: ");
person.setName(stdin.readLine());
stdout.print("Enter email address (blank for none): ");
String email = stdin.readLine();
if (email.length() > 0) {
person.setEmail(email);
}
while (true) {
stdout.print("Enter a phone number (or leave blank to finish): ");
String number = stdin.readLine();
if (number.length() == 0) {
break;
}
Person.PhoneNumber.Builder phoneNumber = Person.PhoneNumber.newBuilder().setNumber(number);
stdout.print("Is this a mobile, home, or work phone? ");
String type = stdin.readLine();
if (type.equals("mobile")) {
phoneNumber.setType(Person.PhoneType.MOBILE);
} else if (type.equals("home")) {
phoneNumber.setType(Person.PhoneType.HOME);
} else if (type.equals("work")) {
phoneNumber.setType(Person.PhoneType.WORK);
} else {
stdout.println("Unknown phone type. Using default.");
}
person.addPhones(phoneNumber);
}
return person.build();
}
// Main function: Reads the entire address book from a file,
// adds one person based on user input, then writes it back out to the same
// file.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.err.println("Usage: AddPerson ADDRESS_BOOK_FILE");
System.exit(-1);
}
AddressBook.Builder addressBook = AddressBook.newBuilder();
// Read the existing address book.
try {
addressBook.mergeFrom(new FileInputStream(args[0]));
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println(args[0] + ": File not found. Creating a new file.");
}
// Add an address.
addressBook.addPeople(PromptForAddress(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)), System.out));
// Write the new address book back to disk.
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(args[0]);
addressBook.build().writeTo(output);
output.close();
}
}
ListPeople.java
package com.sylar.test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import com.sylar.protocol.AddressBookProtos;
import com.sylar.protocol.AddressBookProtos.AddressBook;
import com.sylar.protocol.AddressBookProtos.Person;
import com.sylar.protocol.AddressBookProtos.Person.PhoneNumber;
class ListPeople {
// Iterates though all people in the AddressBook and prints info about them.
static void Print(AddressBook addressBook) {
for (Person person: addressBook.getPeopleList()) {
System.out.println(" Person ID: " + person.getId());
System.out.println(" Name: " + person.getName());
if (person.hasEmail()) {
System.out.println(" E-mail address: " + person.getEmail());
}
for (Person.PhoneNumber phoneNumber : person.getPhonesList()) {
switch (phoneNumber.getType()) {
case MOBILE:
System.out.print(" Mobile phone #: ");
break;
case HOME:
System.out.print(" Home phone #: ");
break;
case WORK:
System.out.print(" Work phone #: ");
break;
}
System.out.println(phoneNumber.getNumber());
}
}
}
// Main function: Reads the entire address book from a file and prints all
// the information inside.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.err.println("Usage: ListPeople ADDRESS_BOOK_FILE");
System.exit(-1);
}
// Read the existing address book.
AddressBook addressBook =
AddressBook.parseFrom(new FileInputStream(args[0]));
Print(addressBook);
}
}
Show Disqus Comments